
The realization of the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) requires technical support. It is the consensus of the international community to take advantage of the opportunities brought about by emerging technologies to accelerate the achievement of the SDGs. The new generation of artificial intelligence (AI), an important symbol of emerging technologies, is crucial for economic and social development as well as the achievement of the SDGs.
The AI for SDGs research project aims to map Chinese enterprises’ AI practices with 17 SDGs, in order to discover the value and development opportunities of AI technology to power SDGs, and explore the path of AI of new generations.
Mapping the SDGs against Chinese enterprises’ AI practices – six findings
In order to further explore Chinese enterprises’ AI practices and their impact on the implementation of SDGs, the project team collected information through multiple channels such as research reports, expert recommendations, mainstream media reports, enterprises’ self-recommendation and official websites, to get relevant policies and industrial analysis of AI. By observing the development of alternative enterprises, the team grasped the principles of AI technology, the implementation process, application effectiveness, as well as the positive and negative effects. 231 AI business cases (as of May 2020) were selected as samples, covering the three dimensions of sustainable development: the economic, social and environmental.
In selecting samples, the project team followed four principles, namely, targeted mapping between cases and SDGs, distinct advantages of AI technology in the implementation of SDGs, AI applications in the real world, and AI applications with quantifiable results, in order to ensure reasonable analysis results.
The research benchmarks Chinese enterprises’ AI practices against the SDGs and visualizes the value and potential of Chinese enterprises to support SDGs by applying AI technology, as well as the relationship and developing trend between AI and SDGs.
However, AI is a cutting-edge technology with rapid development. The study is limited by researchers' knowledge background, case collection channels, selecting and summarizing criteria, data adequacy, data analysis methods, models, etc.; therefore, the study results should have limitations inevitably. Future researchers should further optimize the research model and analysis results on the basis of more case studies.
Classifications of UN SDGs
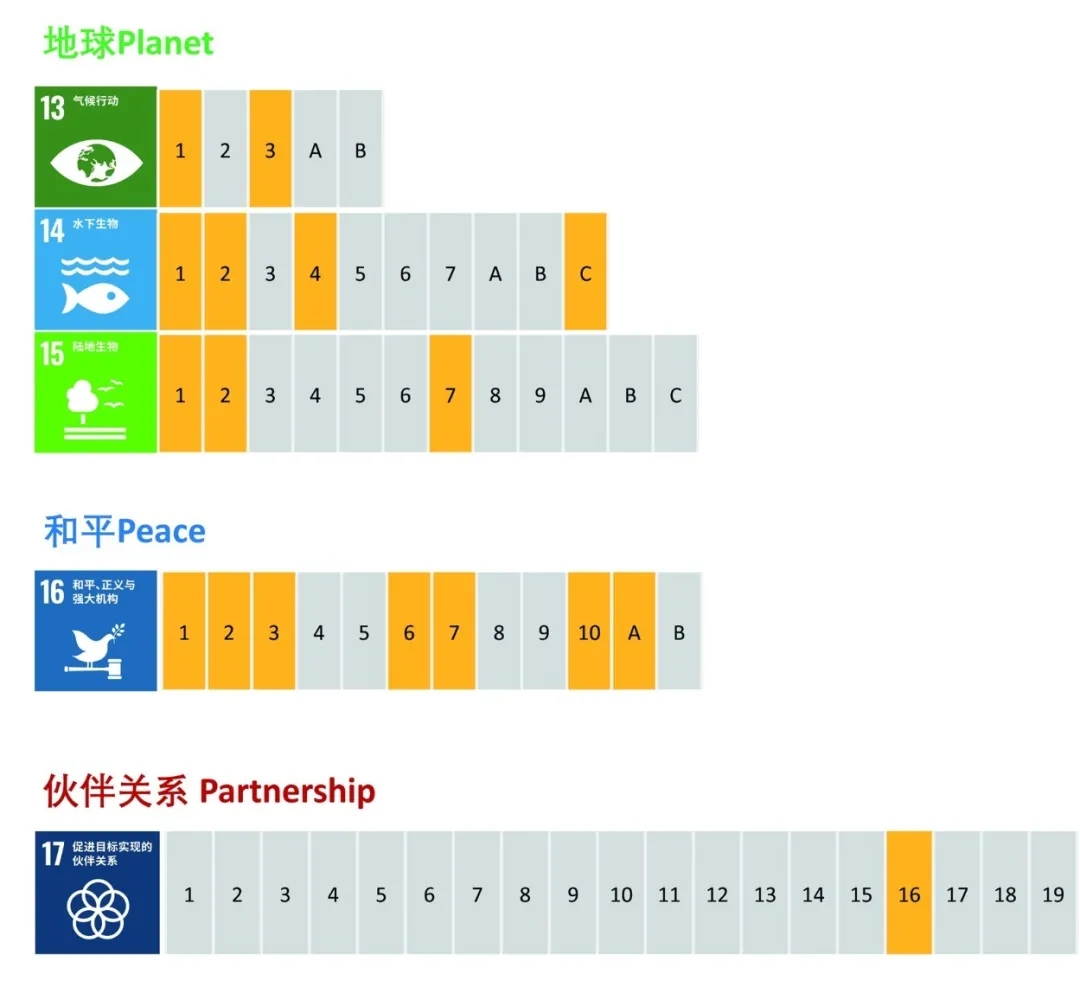
According to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, 169 targets of the 17 SDGs will prompt actions over the next 15 years in areas critical to the people and the planet. The SDGs are interrelated and mutually reinforcing to contribute to a better world. Therefore, on the basis of the three dimensions of sustainable development - economic, social and environmental - the 17 SDGs are further divided based on the five main areas of benefits, in order to be mapped with enterprises’ AI practices.
People: SDGs 1-7
Planet: SDGs 8-12
Prosperity: SDGs 13-15
Peace: SDG 16
Partnership: SDG 17
Analysis of Chinese enterprises’ practices
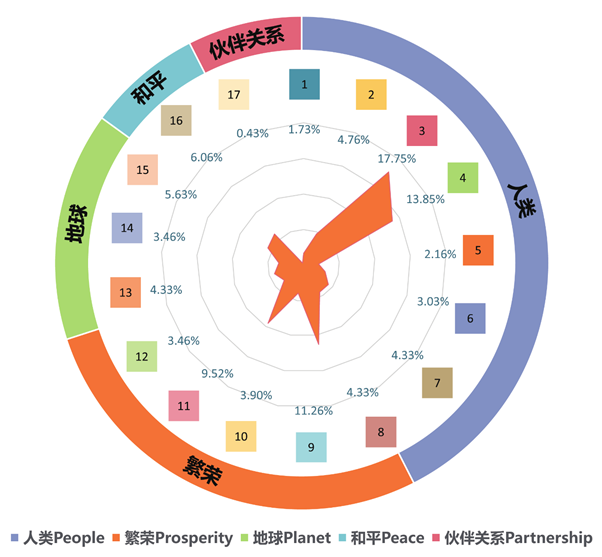
1. Combining Chinese enterprises’ AI practices with SDGs and the AI-assisted SDGs with the presentation of target practices, it can be clearly observed that AI technology has more or less applied practices in the 17 SDGs.
2. Goal 3, 4, 9, 11 are the main destinations of AI technology, such as smart healthcare, smart education, new infrastructure and intelligent transportation. The number of competitors in the industries and AI technology application practices are relatively rich, which has a strong influence on the development of AI market, and gradually shows the value of technology. Areas such as imaging medical market become the blue ocean of AI technology.
3. Goal 1, 5, 6, 12, 17 involve poverty alleviation, equality, environment, mutual assistance between countries. How AI can contribute to these areas is not completely clear, and it is relatively hard to apply AI technology. This may contain new opportunities in new economic growth, which would also be the future direction of AI’s role in the society and the economy.
4. Generally speaking, AI industry is still booming. The scope and depth of impact on the SDGs are expanding year by year as the market competition becomes more intense, with the realization of the research and development of multiple AI technology categories.
5. More and more domestic technology giants are playing the ecological chain game in AI field, and are committed to creating multi-industry AI solutions. The application of their technology plays an important role in many aspects of SDGs. While most AI start-ups focus on vertical industry solutions, AI technology is more prominent in one single field, so are the corresponding SDGs.
6. Due to the lack of effective regulatory and ethical restraint mechanisms, some enterprises do not pay enough attentions to ethical issues like privacy protection, resulting in negative information and impact on technology applications, so that some AI technologies and practices may even reverse the implementation of the SDGs.
Six suggestions
1. Strengthen industry-university-research-government cooperation
While more and more research institutions are shedding lights on SDGs and the common sense of AI for SDGs is emerging, implementation still needs collective efforts. A government-led, industry-guided, experts-supported and enterprises-involved development mode is necessary. On one hand, all parties need to reach a consensus, realizing that AI for SDGs is an important way to drive technology for good and a reveal of how tech companies undertake social responsibility and achieve social value. On the other hand, different organizations should leverage their strengths, take actions and unite together to provide businesses with guidance and reference.
2. Develop an action guide to facilitate implementation
We advocate open-souring and sharing, and encourage all parties including industries, universities, research institutions and consumers to jointly compile an AI for SDGs action guide to provide guidance for Chinese enterprises and accelerate the SDG implementation process by Chinese AI application. Only AI for SDGs is advanced could we achieve the “SDGs-centered intelligence” goal, and realize the vision of benefiting the mankind in the best possible way.
3. Enhance AI enterprises’ awareness to connect AI technology with SDGs proactively
AI for SDGs is an important way to implement the “tech for good” to corporate development. It also reveals the CSR commitments as well as the comprehensive value of innovative AI enterprises, who should enhance awareness of sustainable development and connect AI technology with SDGs. These enterprises should continue to explore broader and deeper beneficial areas, especially those in which AI technology has been barely applied. In this case, corporates profits and social benefits can be realized simultaneously to drive the implementation of SDGs and healthy development of AI.
4. Establish a sustainability committee within enterprises to improve AI governance
Guided by the sustainability idea, enterprises are advised to set a diversified ethical, social responsibility or sustainability committee consisting of scientists, business leaders and legal advisers. An internal mechanism should be set to recognize, evaluate, manage, monitor and report the potential ethical risks of AI from the beginning of research and design and running through the entire life cycle.
5. Enhance publicity to win social attention
As for now, the majority remains concerned about AI development and has not formed a comprehensive understanding of the relationship between AI and SDGs. Governments, academics, industries and media are advised to launch AI for SDGs publicity campaign widely, to increase general understanding of the ideas, practices and values. They should also monitor that whether AI technology complies with the requirements, goals and principles of SDGs.
6. Understand the limitations of AI technology and create a negative list
Both UN reports and academic research have warned that while having brought great changes, AI also poses challenges to efficiency and equity, which may trigger moral and ethical problems and generate negative impacts on SDGs. In this case, AI-related enterprises should notice and analyze the side effects and limitations of AI technology as tool. Apart from guiding the right direction, organizations need to make a negative list of AI practices that may have severe negative impacts and offer relevant suggestions.
This article is one of the results of the "AI for SDGs" research project, which is jointly carried out by China Sustainability Tribune and China Intelligence Industry Alliance, under the guidance of Science and Technology Department, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. The article is directed by project leaders Yu Zhihong and Lin Bo, written by Wu Yanan, Xiao Xiao, Du Juan and Wang Qiurong.


 Back
to top
Back
to top